
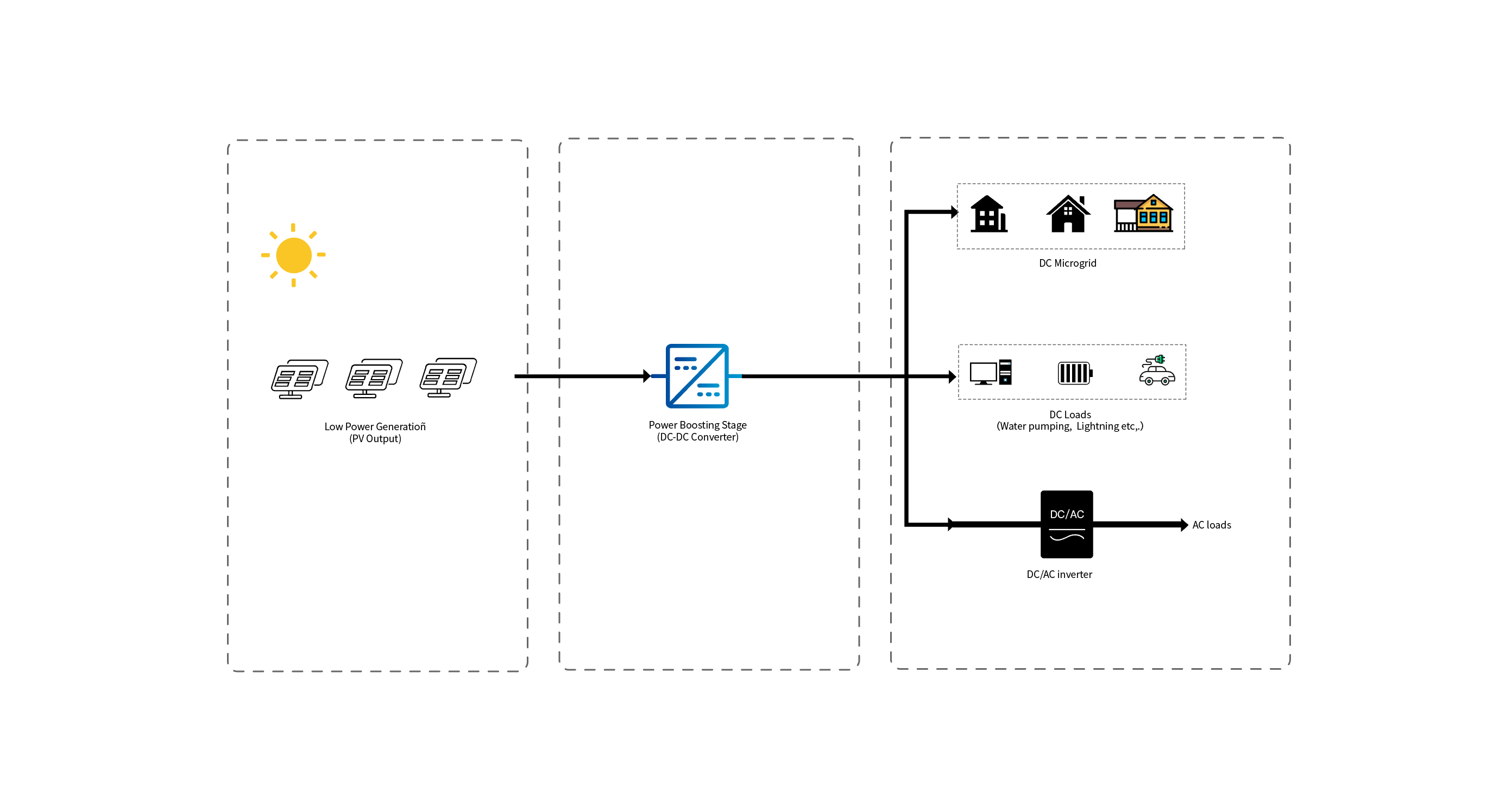
Energy storage DC-DC converters are key power conditioning devices that connect batteries (or other energy storage media) to the AC grid (via an inverter) or DC loads. Their core function is to enable controlled bidirectional flow of electrical energy and flexible conversion of voltage levels.
Key advantages
When must it be used?
Summarize
1. Voltage Matching and Optimized Operation
Key Function: Battery voltage varies significantly with state of charge (SOC) and charge/discharge current. DC-DC converter can stably boost or buck this wide, unstable battery voltage to the stable voltage level required by the inverter or DC bus.
Benefit: This ensures the inverter always operates within the optimal input voltage range, thereby maintaining overall system efficiency and stability and preventing system downtime due to low battery voltage.
2. Enable Bidirectional Energy Flow
Key Function: Energy storage systems must be able to both charge (drawing power from the grid or photovoltaics) and discharge (supplying power to the grid or loads). Bidirectional DC-DC converters enable efficient bidirectional energy flow through control algorithms without changing the hardware topology.
Benefits: Simplifies system architecture and improves reliability, making them essential features for energy storage systems.
3. Precise Charge and Discharge Management
Key Function: The DC-DC converter enables high-precision, fast-response control of the battery's charge and discharge currents. This means it can strictly execute the instructions of the battery management system (BMS), enabling various charging modes such as constant current, constant voltage, and constant power.
4. Enhanced System Flexibility and Compatibility
Key Benefit: The DC-DC link allows for greater flexibility in battery pack voltage selection and system design. It can accommodate battery packs of varying voltage levels (such as low-voltage battery pack paired with a high-voltage inverter), facilitating future expansion or battery type changes.
Benefit: It eliminates the rigid voltage matching between batteries and inverters, opening up more possibilities for system design.
5. Improved Safety (Especially for Isolated Topologies)
Key Role: Using an isolated DC-DC converter (such as a topology with a high-frequency transformer) can achieve electrical isolation between the battery pack and the grid.
Benefit: Effectively prevents DC-side faults (such as short circuits) from endangering AC-side equipment and personnel. It also suppresses common-mode interference, improving the system's electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) performance.

Application Scenario | Is it necessary | Reason |
|---|---|---|
The battery voltage does not match the inverter DC input voltage | must | For example, a low-voltage battery pack (such as 48V) needs to be boosted to a high-voltage inverter bus (such as 700-800V). |
Requires strict battery current control and protection | must | Achieve precise constant current/constant power control to maximize battery life and safety. |
The DC side requires electrical isolation | must (isolated type) | Safety regulations may require suppression of leakage current or enhancement of EMC performance. |
Photovoltaic and storage integrated system | Usually required | Coordinate the different voltages and power flows between photovoltaic panels, batteries and inverters. |
When you use DC-DC converters, you can connect different types of batteries and devices without worrying about voltage problems. This makes your energy storage system more flexible and easier to manage.
• In summary, the advantages of DC-DC energy storage lie in its provision of essential core functions such as voltage matching, power control, bidirectional flow, and safety isolation, making it key to building high-performance, high-reliability energy storage systems.
• Its disadvantages lie in the additional cost, energy loss, and system complexity it introduces.
Current technological development trends are focused on developing DC-DC converter topologies and control strategies (such as soft switching technology and the use of wide-bandgap semiconductor devices) with higher efficiency, higher power density, and lower cost, to maximize its advantages while minimizing its disadvantages.